Introduction to Neutralization Reactions
A neutralization reaction is a double displacement reaction. There are four different neutralization reactions:
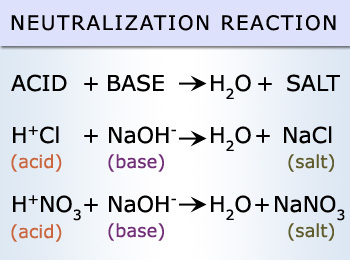
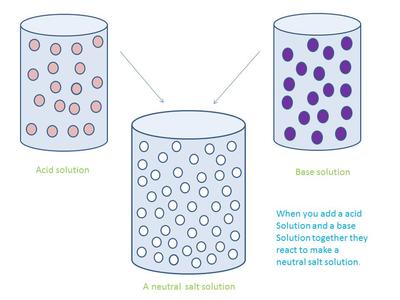
1. Acid + base --> salt + water
Example: H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 --> CaSO4 --> H2O
- In an acid base reaction H+ ions combine with OH- ions to form H20 (water.)
H+ + OH- = H2O
-Non metal ions from the acid and metal ions from the base combine to form a salt.
2. Acid + alkali --> salt + water
Example: HCl + NaOH --> NaCl + H₂O
- In an acid alkali reaction H+ ions combine with OH- ions to form H20 (water.)
H+ + OH- = H2O
-Non metal ions from the acid and metal ions from the base combine to form a salt.
3. Acid + metal --> salt + hydrogen
Example: H2SO4 + Mg --> MgSO4 + H2
- Mg (metal) is dissolving in the acid to form the products of the neutralization reaction.
4. Acid + metal carbonate --> salt + water + carbon dioxide
Example:2HCl + CaCO3 --> CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
- CaCO3 (metal carbonate) is dissolving in the the acid to form the products of the neutralization reaction.
1. Acid + base --> salt + water
Example: H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 --> CaSO4 --> H2O
- In an acid base reaction H+ ions combine with OH- ions to form H20 (water.)
H+ + OH- = H2O
-Non metal ions from the acid and metal ions from the base combine to form a salt.
2. Acid + alkali --> salt + water
Example: HCl + NaOH --> NaCl + H₂O
- In an acid alkali reaction H+ ions combine with OH- ions to form H20 (water.)
H+ + OH- = H2O
-Non metal ions from the acid and metal ions from the base combine to form a salt.
3. Acid + metal --> salt + hydrogen
Example: H2SO4 + Mg --> MgSO4 + H2
- Mg (metal) is dissolving in the acid to form the products of the neutralization reaction.
4. Acid + metal carbonate --> salt + water + carbon dioxide
Example:
|
Feel like you already know everything?
|